A gastroenterologist is a specialist in gastrointestinal diseases. Gastroenterologists treat all the organs in your digestive system, including your GI tract (esophagus, stomach, and intestines) and biliary organs (your liver, bile ducts, pancreas, and gallbladder). Some possible areas of emphasis are:
Pancreatic disease
Inflammatory bowel disease, or chronic inflammation of the digestive tract
Gastrointestinal cancer
Endoscopic surveillance
Reflux esophagitis, which is commonly due to GERD
What isa gastroenterologist?
Gastroenterologistsbegin as general physicians. After completing three years of medical residency they can treat all kinds of diseases and conditions related to the digestive system. A gastroenterologist may work with:
Hepatologists, who specialize in the liver
Radiologists, who specialize in imaging
Oncologists, who specialize in cancer
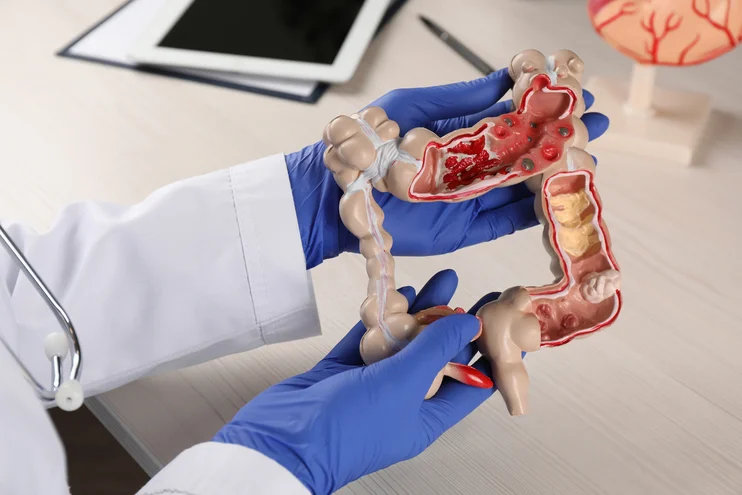
What part of the body does a gastroenterologist focus on?
“Gastro” means stomach, “enter” means intestines, and “ologist” means specialist, referring to the stomach and intestines. Although these organs commonly are involved in gastrointestinal diseases, your mouth and esophagus are also part of your digestive system. These parts of the body include the:
esophagus, or food pipe
stomach
small intestine
colon
rectum
pancreas
Types of Gastroenterology Diseases
Gastroenterology includes all the digestive system’s diseases. These are the most common diseases including colon cancer, constipation, acid reflux, diarrhea, liver cirrhosis, hepatitis, hemorrhoids, irritable bowel syndrome, stomach cancer, pancreatitis, gas, Crohn’s disease, lactose intolerance, etc.
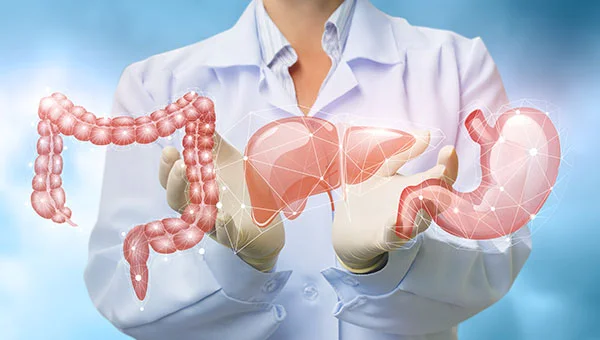
Procedures for Gastroenterology Disease Diagnosis
The digestive tract comprises all the organs from the mouth to the anus, therefor there are multiple procedures to perform gastroenterology disease diagnosis. Your doctor will need to determine the origin of your problem to diagnose it. Some of these procedures include:
GI endoscopy is used to test the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine in the upper part.
The larger intestine (colon) is examined by colonoscopy.
Enteroscopy is used in the small intestine's internal depths.
Non-surgical treatment of hemorrhoids is infrared coagulation therapy (IRC).
The last portion of the colon and the rectum is looked at through a flexible sigmoidoscopy.
Abdomen X-rays are also used to detect stomach problems.
What conditions do gastroenterologists diagnose and treat?
Gastrointestinal diseases that affect your stomach and intestines, such as:
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
Celiac disease
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO)
Food allergies and intolerances
Stomach ulcers
Esophageal disorders, such as:
Swallowing difficulties
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Esophagitis
Hiatal hernias
Liver diseases, such as:
Viral hepatitis
Toxic hepatitis
Fatty liver disease
Cirrhosis
Pancreatic, biliary, and gallbladder diseases, such as:
Gallstones
Cholecystitis
Pancreatitis
What symptoms should I tell my gastroenterologist about?
You might come to a gastroenterologist with common gastrointestinal symptoms, such as:
Abdominal pain
Bloated stomach
Indigestion
Gas and gas pain
Nausea and vomiting
Rectal bleeding
What procedures do gastroenterologists perform?
Gastroenterologists perform a range of nonsurgical procedures. This can include:
Upper endoscopy, which helps diagnose conditions of the food pipe, stomach, and small intestine
Endoscopic ultrasounds, which examine the upper and lower GI tract, as well as other internal organs
Colonoscopies, which can detect colon cancer or colon polyps
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, which identifies stones or tumors in the bile duct area
Sigmoidoscopy, which evaluates blood loss or pain in the lower large bowel
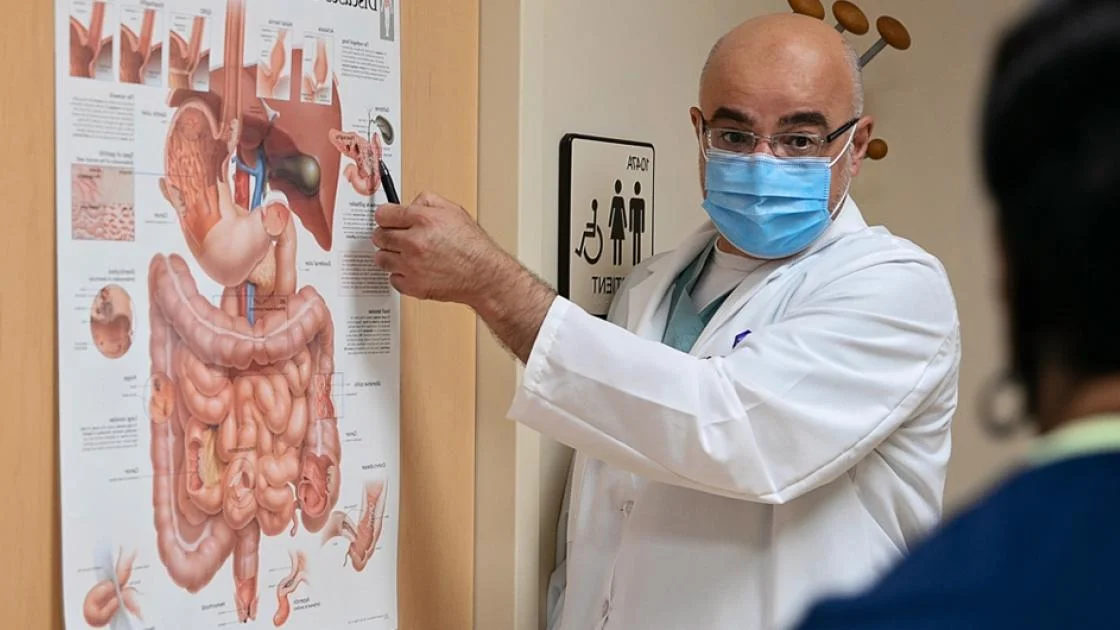
Do gastroenterologists treat cancer?
A gastroenterologist is likely to be the first to discover if you have cancer in any of the organs of your digestive system. Through endoscopy and biopsy, gastroenterologists locate, remove, and identify cancerous tumors throughout your GI tract and biliary system. In some cases, gastroenterologists can treat certain tumors through the endoscope, either by dissecting them or by targeting them with lasers. Gastroenterologists may diagnose, stage, or treat:
Stomach cancer
Colorectal cancer
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors
Duodenal cancer
Small intestine cancer
Esophageal cancer
Conclusion
Gastroenterology, the branch of medicine focused on the digestive system and its disorders, is an essential field that addresses a wide spectrum of conditions affecting the gastrointestinal tract. From common ailments like gastroesophageal reflux to complex diseases such as Crohn's and celiac disease, gastroenterologists play a crucial role in diagnosing, treating, and managing digestive health. The advancements in this field, including endoscopic techniques and a deeper understanding of the gut microbiome, continue to enhance patient care. As research progresses, gastroenterology promises to deliver even more innovative treatments, improving the lives of patients with digestive disorders and contributing to the broader understanding of human health.